A River Runs Through It, 2021, oil, acrylic, resin, aluminum, fishing line, fishing hooks, wood, nails, cigarette butts, graphite, glass flakes, lipstick, hinge, ink, canvas on shaped panel, by Chloe Chiasson © The artist. Courtesy Albertz Benda Gallery
The Worm Charmers
A Florida family coaxes earthworms from the forest floor
By Michael Adno
A hint of blue on the horizon meant morning was coming. And as they have for the past fifty-four years, Audrey and Gary Revell stepped out their screen door, walked down a ramp, and climbed into their pickup truck. Passing a cup of coffee back and forth, they headed south into Tate’s Hell—one corner of a vast wilderness in Florida’s panhandle where the Apalachicola National Forest runs into the Gulf of Mexico. Soon, they turned off the road and onto a two-track that stretched into a silhouette of pine trees. Their brake lights disappeared into the forest, and after about thirty minutes, they parked the truck along the road just as daylight spilled through the trees. Gary took one last sip of coffee, grabbed a wooden stake and a heavy steel file, and walked off into the woods. Audrey slipped on a disposable glove, grabbed a bucket, and followed. Gary drove the wooden stake, known as a “stob,” into the ground and began grinding it with the steel file. A guttural noise followed as the ground hummed. Pine needles shook, and the soil shivered. Soon, the ground glowed with pink earthworms. Audrey collected them one by one to sell as live bait to fishermen. What drew the worms to the surface seemed like sorcery. For decades, nobody could say exactly why they came up, even the Revells who’d become synonymous with the tradition here. They call it worm grunting.
Audrey and Gary Revell took to each other in high school. In 1970 when Gary graduated, he asked Audrey to be his wife, and they married at his grandfather’s place down in Panacea, about thirty miles south of Tallahassee. For his entire life, he’d lived on an acre six miles west of Sopchoppy, Florida, in an area known as Sanborn. The place is set deep in the heart of the Apalachicola National Forest, a vast expanse of flatwoods and swamp that covers over half a million acres struck through with rivers. It’s where he and his siblings grew up in an old church building, where his great-grandfather had settled after finding his way up Syfrett Creek into the wilderness. It’s where Audrey and Gary settled after their wedding. “I was only sixteen, so I feel like I grew up here,” Audrey told me. Soon after, they started looking for ways to make ends meet, and Gary suggested, “We might ought to look into that worm thing.”
His family was already deep into worm grunting. Three generations preceded him, and by 1970, his uncles Nolan, Clarence, and Willie weren’t only harvesting the worms to sell as bait but were working as brokers with their own shops that distributed the critters throughout the South. It didn’t hurt that Audrey fell in love with it immediately. The work was seasonal, busiest in spring. During other parts of the year, their family trapped for a living, dug oysters, logged, raised livestock, and set the table with what they grew in their yard or caught in the water or in the forest. “That’s how we learned the woods,” Gary said. “We went in every creek, water hole, pig trail. You name it.”
By the 1970s, the cottage industry had reached its peak. Then Charles Kurault arrived in 1972 to film a segment for his eponymous CBS show, On the Road with Charles Kurault. The attention led the Internal Revenue Service and the U.S. Department of Agriculture to start regulating the harvest of worms, investigating unreported income, and implementing permit requirements. Back then, the sound produced by grunters in the first hours of daylight was as common as birdsong in this forest, and hundreds of thousands of worms were carried out in cans. Folks who once turned to grunting to make ends meet seasonally were soon in the woods year-round during that decade, competing to summon the bait to the surface and sell to brokers among the counties set between the capital city and the Apalachicola River. Millions of worms left those counties bound for fishing hooks across America. Money followed the pink fever, but as with any rush, the demand eventually dimmed as commercial worm farms caught on and soft, plastic lures became popular.
By that point, Audrey and Gary had decided to shape their own outfit. His uncles had told them, You ought to just think about keeping all that money to yourself. The couple had grown tired of depending on others for work. So, they set up their own shop full time, cultivated clients as far away as Savannah, and delivered bait all over the South, driving it themselves, or sending it north in sixteen-ounce, baby blue containers via Greyhound buses. “All the money was coming our way, what little we made,” said Gary. “We struggled with it for a long time, because when you get off the grid like that and try to do it for yourself and you’re young, it’s hard.”
I wanted to know what spending their life in the woods hunting for worms meant, but I also wanted to know where this mysterious, artful tradition came from. In the UK, there are a handful of worm-charming competitions and festivals in Devon, Cornwall, and Willaston that began in the 1980s and another in Canada that started in 2012. I’d heard of similar events in east Texas, of people using pitchforks and spades as well as burying one stick in the ground and rubbing it with another to coax worms up to the surface. Later, I even found a newspaper clipping from 1970 reporting on the first International Worm Fiddling Championship, in Florida. I searched for a deep well of literature on the practice but found nothing. Certainly, worm grunting predated the Revells. But why did rubbing a stick stuck in the ground with a metal file conjure earthworms? The only way to understand was to follow the Revells into the woods.
In February, I carved out toward the Revells’ place from St. Teresa, a strip of homes along the Gulf coast. Going first through Tate’s Hell, then turning west through the tiny town of Sopchoppy, I slipped into the forest as the distance between each home grew wider and wider. I found myself in a sea of slash and longleaf pine. Six miles later, I met Gary Revell in his driveway beneath an eastern redbud throwing its first spray of pink flowers. “Morning, Mike,” he said with a contagious warmth. In their kitchen, I met Audrey, who had already poured a cup of coffee, set out milk and creamers, and had a jar of sugar in hand. A few minutes later, we piled into their truck and drove down a narrow vein of road near Smith Creek. A horned owl drew a line through the trees, where the yellow flowers of Carolina jessamine crawled over palmettos. Black water pooled in ditches alongside the narrow road lined with bald cypress and the periodic sweet bay magnolia. By the time we reached where we were going, I had no sense of how far we’d gone or where we were.
Although the northern borders of the Apalachicola National Forest press right up against the Tallahassee airport, the place is remote. Across nearly six hundred thousand acres, you could spend lifetimes trying to map its dizzyingly vast flatwoods, hydric hammocks, and cypress stands. Two hundred and fifty million years ago when our contemporary continents formed, Florida’s peninsula broke off a fault line belonging to what’s now West Africa; they share the same basement rock today. Fifty-six million years ago, as sea levels receded, the Suwanee Current flowed from the Gulf of Mexico across what’s now Florida’s panhandle, bisecting Georgia before running into the Atlantic. And over the next twenty million years, Florida appeared first as an island separated from North America by a sequence of patch reefs before sea levels continued to fall and a bridge formed with Georgia, revealing this very forest. A few thousand years later, the bones of the southern Appalachians, ground into dust by glacial erosion, washed out of the Apalachicola River Valley and formed barrier islands that rim Apalachee Bay today. That river carried sediment down through Georgia and into the Gulf, which flanks the western edge of the forest. And as you move east, the New River, the Ochlocknee River, and the Sopchoppy River flow through the forest made up of two districts. An archipelago of sinkholes and hardwoods is lacerated by thin roads that mirror oxbows in the rivers. In 1936, when the land was declared a national forest, it became one of America’s southernmost pockets of wilderness and among the world’s most unique ecosystems. As the Revells told me, many are afraid of the place, scared to step foot out of the car. “I’ve walked all over all these woods, so I love them,” Audrey said. “A lot of times when we’ll be going to work in the mornings, we won’t meet a single car. It’s just nice being out here mostly alone. You know?”
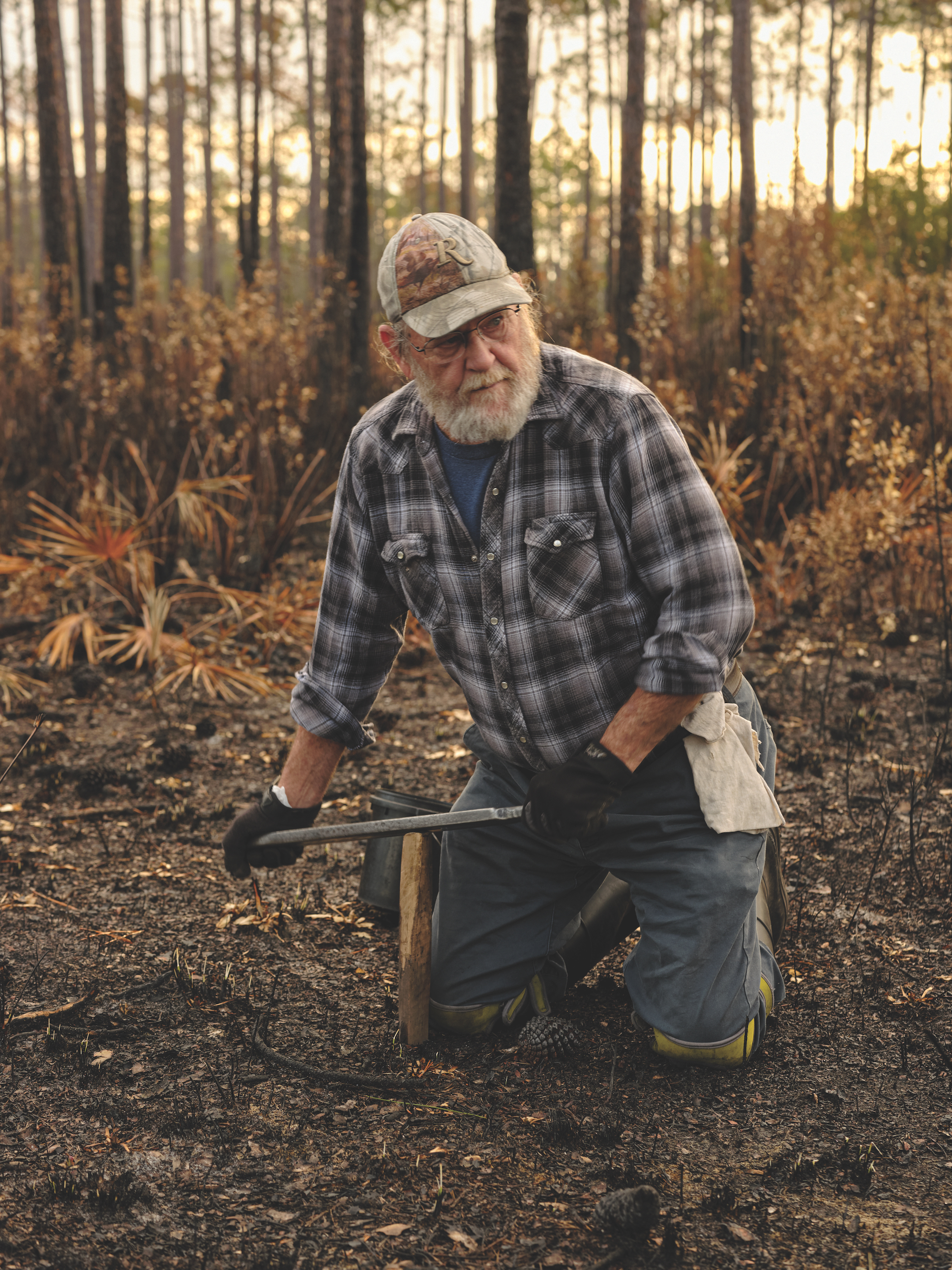

Gary Revell roops in a stand of recently burned trees in the Apalachicola National Forest just after daybreak. Photograph by Michael Adno
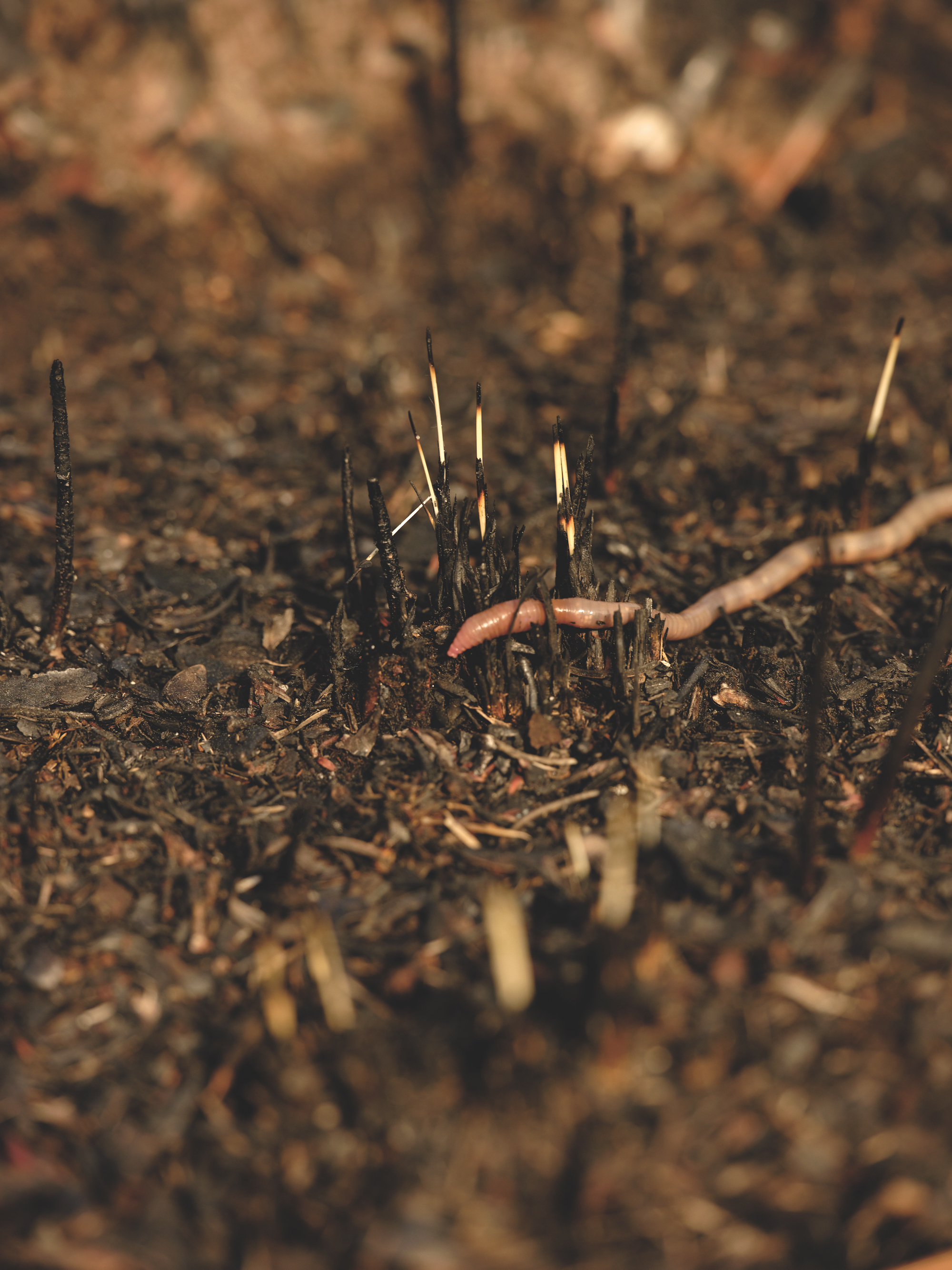

A native earthworm, diplocardia mississippiensis, crawls across the ground before Audrey Revell collects it by hand. Photograph by Michael Adno
That first morning I spent with them, the Revells made their way to a part of the woods called Twin Pole. The forest service had recently burned a block of woods there, which meant the ground would be clear and easier to work. As we got closer, I could smell the sweet fragrance of smoldering slash pines and palmettos. For centuries, pine scrub and prairie throughout the South has burned naturally and been torched deliberately, first by Indigenous peoples like the Timucuan or Apalachee and then later by ranchers and land managers to replenish the soil and promote growth. Worm grunters follow the forest service’s burns like a compass, as the open ground makes it easier to spot worms and avoid venomous snakes.
“Alright, Mama,” Gary said to Audrey before changing into a pair of boots, fastening knee pads, and slipping on gloves. We walked through the burnt palmettos, coated in a film of black soot, before he pointed to a few holes in the soil. They were clues to where worms were and where they were headed. He took his stob, one his son had hewn out of black gum, and knocked it a foot into the earth with his steel file before rubbing the file against the stob’s head. He called each pass a “roop.” With every roop, he mirrored the sound himself, groaning first in a low pitch then ascending to an abrupt stop. Gary would roop, pause, tell a story, then start again. It didn’t take long before a dozen large earthworms began crawling around the earth between us as Audrey gathered them by hand.
“Gary can call up any kind of animal,” Audrey said. Screech owls, ducks, even a bull they once came across in the woods. Once, after he called to a quail, Audrey swears the bird landed on his head. I looked down as Audrey picked up worms and could see this was a corollary. As Gary rooped and talked, Audrey drew concentric circles around him, picking up the largest worms and carefully placing them in a one-gallon paint can. Audrey noted the difference between worms—“milky” that are lighter in color and frail, and dark pink worms that last longer on the shelf. Gary roops most of the time, but Audrey does sometimes, too. “They’re coming up tail first,” Gary said. He gazed down and read the ground: Here were some castings left by worms; some mounds of fresh earth; a transition in the ground that meant prime moisture. The Revells’ intuition was like that of the fishermen they were collecting bait for, a catalog of knowledge assembled from spending time out here and bound together by deep curiosity. Gary knocked his stob down against the serpentine root of a palmetto and demonstrated how to change the pitch. “When I see that,” he said, pointing to some larger holes, “I know he’s right here somewhere close.”
With a couple of paint cans filled, about 500 worms in each, Audrey and Gary headed back to their truck, collecting scraps of trash and some firewood along the way. An hour later, they dumped their catch out in a shed where they store their worms, counting them out by hand and then placing them in five-gallon buckets filled halfway up with sawdust they collect in the forest. Folks that know them come and collect worms from the shed themselves, leaving the money they owe in a box on the wall. Often, they’ll leave notes scrawled on pieces of cardboard, check registers, and even a cast-off piece of packing tape that read, “I got 200. I paid back the ten I owe.”
For two convenience stores in Wakulla County, Audrey and Gary are the source for worms. At home, they pack the bait in clear plastic cups with baby blue caps and deliver them each week. In the decades since the Revells struck out on their own, the market has winnowed with the advent of artificial baits and farmed nightcrawlers, and so have the venues to sell worms. In good years, they earned $30,000, according to a 2009 piece in the Tampa Bay Times, but they told me they didn’t want to discuss what they make today. Some years, they harvested oysters for part of the winter and then baited throughout the warmer months. The two found their way through, together, even when bad weather, drought, and competition reshaped the way they worked. They started traveling farther into Liberty County, hiking deep into the flatwoods to avoid previously worked pieces of land. In summer, when the temperature turned mean, they worked Tate’s Hell at night. “This earthworm deal is something that you got to live with and stay on top of to be able to survive it,” Gary said, “and we can say we’ve lived a very good life.” They’d raised their two sons this way, spent their lives living with the forest, watching almost every sunrise out there together. “It ain’t been no easy deal, but there’s really nothing on earth I’d trade for it,” Gary said. Today, one of the Revells’ sons, who is now forty-eight, marks the fifth generation of their family collecting the pink currency from the forest.
In the nineteenth century, Gary’s great-great-grandfather paddled up the Ochlocknee and into a branch that bent into the trees before it dissolved into a shallow stream. Audrey and Gary live in that area today, near a creek named for one side of his mother’s family, the Syfretts. As kids, Gary and his two brothers, Lucious and Donald, came up in the woods, often passing the days with three cousins opposite the creek from them. “We didn’t have a lot of people around, but we had this forest, and that kept us occupied.” Their father, Frank, was an equipment operator for the county during the week, but worked alongside his brothers on the weekends, grunting in the forest at first light. Fifty years ago, he could earn as much as a hundred dollars in two days of baiting, which dwarfed what he made in a week for the county, roughly eight hundred dollars in today’s money. Gary tagged along any chance he got. That’s how he first heard the tale of his great-grandfather’s worm discovery in the 1940s. Living along the Ochlocknee River, his great-grandfather fished often, and developed a sense of what baits worked where and when. While repairing his car one day, he’d left it running, jacked up the chassis, and removed a wheel. As the tire rolled away and his eyes followed it, he saw the ground strewn with pink worms.
As the story goes, his great-grandfather tested the theory elsewhere, leaving the car to idle and seeing worms sprout up on the spot. It was clear the vibrations stirred the worms, making it easier to collect bait and therefore sell it. This is how the mysterious practice became central to the Revells’ lives.
Later, the men noticed worms appearing when they chopped wood or ran saws against saplings. Gary remembered using an axe handle as a stob, rubbing the blade of another axe against it. Some folks in north Florida called it worm fiddling, worm rubbing, worm snoring, worm charming, and, of course, worm grunting. Styles and materials for coaxing worms to the surface varied. Some people preferred hickory stobs and used steel leaf springs from cars as a file. The Revells used different-shaped stobs for different sorts of soil, but they always used black gum, persimmon, or cherry wood, and preferred flat, thick steel files.
What’s strange is that despite the widespread practice of worm grunting, I couldn’t find a definitive origin story. There wasn’t a deep well of folklore to draw from online: not in the University of Florida’s special collections archive, the Florida State University archives, or those of Florida Agricultural and Mechanical University. I searched my copy of the Federal Writers’ Project’s guide to Florida, organized by Stetson Kennedy and partially written by Zora Neale Hurston, with no luck. I couldn’t find anything that went farther back than the 1970s. But after another pass through the newspapers at the University of Florida, I found a path that stretched back more than a century.
On Friday, July 16, 1946, the Bradford County (FL) Telegraph ran a front-page item, “Know Anything about ‘Worm Grunting’?” They asked readers to submit letters, offering a five-dollar prize for “the best replies to a series of questions on this fascinating subject.” Among them: how long had the practice existed, who told them about it, where they grunted, what they looked for, what they used, and what time was best to do it. Three months later, the paper published six letters. Dave Crawford from Starke wrote that he’d learned of it in 1933. Some claimed that it had existed at least since 1896, another since 1866, while one reader claimed it had been around in some form since 1786. One man wrote, “When I was a small boy, there was an old colored woman that worked for us. In the afternoon she would take me out and teach me to grunt for worms. She told me her mother taught her to grunt worms.” Those anecdotal accounts raised the question of whether this was a tradition that extended back to the period of chattel slavery in America or even farther, before Indigenous peoples were forced from the land that settlers would come to call Florida.
The Revells’ tales of grunting echoed those long-ago anecdotes. Readers referenced an axe handle method, or crosscut saws, and an iron and a stake—all before Audrey or Gary were born. The winning letter from Dave Crawford revealed a bit of poetry and intuition that grunters still practice today: “When the wen is from the west the werms come up good and when you see the birds feeding on the ground and the red heads flying from tree to tree you can grunt up better. Just get a old ax or tire iron and a good pine stob about 2 feet long and a old lard bucket and get down by the swamp where it is wet and boy go to rubing and get busy and grunt long and loud and the old boys will come out they hiding place.”
That tradition endures, largely unchanged here in the Apalachicola National Forest. Yet, it’s vanishing like so many other foodways, forms of heritage, and ways to earn a living in this part of the country. Lots of folks preferred this work to other forms of labor, such as driving an Uber in town or food delivery, but commercial fishing, crabbing, and the shrimp industry have shrunk with each passing year due to increasing regulation, depleted fisheries, climate change, and cheaper imported seafood. The same is true for oyster harvesting, once a mainstay of the region’s foodways. After years of oyster decline partly due to overharvesting and negligent water management, in 2020 the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission mandated a five-year halt in harvesting oysters from the Apalachicola Bay. It was part of a $20 million plan to restore the habitat and population. That ban promised to leave local oyster tongers without work until 2025. As for worm grunting and its slow decline, the passage of time is responsible, too. “All the old people is gone,” Gary said. “That was the key to the whole thing. They set it up.”
In 2002, a committee was organized to preserve the tradition and put on the first annual Sopchoppy Worm Gruntin’ Festival. Every second Saturday in April since, Rose Street and Winthrap Avenue fill with vendors, bands, and demonstrations. There’s a ball and an annual queen. Media outlets flock to Wakulla County to cover the festival, often centering the Revells in their pieces. In 2009, they appeared on the Discovery Channel’s Dirty Jobs. That same year, Jeff Klinkenberg profiled the Revells for a cover story in what is now the Tampa Bay Times. Nobody could say definitively why the worms responded to vibrations, though, until a neuroscientist arrived in Sopchoppy with a theory.
As a kid in Maryland during the 1970s, Kenneth Catania had a curiosity about the woods near his home that shaped his career path as a neuroscientist with a bent toward ecology and biology. His obsession with moles came later during a job at the National Zoo in Washington, D.C. And that obsession eventually grew into a dissertation on star-nosed moles, which revealed how their sensory cortex evolved and developed to process information. This, by proxy, revealed how all mammals’ senses evolved. In 2006, he earned a MacArthur Fellowship or “Genius Grant.” The award came with $500,000. Two years later, he headed for the Apalachicola National Forest, thinking that the moles there might help him unravel another mystery about a different group of underground creatures.
For years, he’d wanted to visit the worm festival in north Florida, but annual field work always overlapped. Finally, in 2008, he drove to meet the Revells in Sopchoppy. He arrived with a question shaped by a few sentences written a century earlier by Charles Darwin about worm behavior as it related to moles.
Darwin published his last book in 1881, The Formation of Vegetable Mould Through the Action of Worms With Observations on Their Habits. A sentence that struck Catania read, “It has often been said that if the ground is beaten or otherwise made to tremble, worms believe that they are pursued by a mole and leave their burrows.” Darwin continued, “Nevertheless, worms do not invariably leave their burrows when the ground is made to tremble, as I know from having beaten it with a spade, but perhaps it was beaten too violently.” Seventy years after Darwin’s shovel experiment failed, Dutch biologist and Nobel Laureate Nikolaas Tinbergen claimed that herring gulls tapped their feet to drum up worms, employing “exploitative mimicry.” By 1982, evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins had built off that notion, staking claim to the idea of “rare enemy effect,” by which predators cast themselves in the role of another predator to exploit their prey’s behavior.
Then in 1986, a paper by John H. Kaufmann of the University of Florida drew a connection between wood turtles’ stomping to draw worms to the surface and the work of worm grunters. “Many humans collect earthworms for fish bait by hammering or scraping on a stake driven into the soil…. There is now evidence that wood turtles, Clemmys insculpta, use the same principle in obtaining earthworms for food,” Kaufmann wrote. He also noted an earlier paper from 1960 by Tinbergen that identified a corollary in herring gulls among other birds like flamingos and geese that drummed up prey by “paddling.” Especially fascinating is that Tinbergen hypothesized that the worms mistook the birds’ paddling for the vibrations of a mole. “That’s what drew me down there,” Catania told me. He wondered whether worm grunters were unintentionally mimicking a predator, possibly a mole like Darwin and Tinbergen suggested. “Nobody had formally studied it,” he said.
On that first morning in Florida, Catania’s alarm woke him at five. He got ready and met the Revells, who charmed Catania immediately as he took a seat in the cab of their truck. As they drove into the forest, he thought of this Darwinian theory that shaped his own hypothesis: that earthworms had developed an escape response to vibrations caused by a foraging mole. “What’s beautiful about the system there is the earthworms are native, so they evolved there, and if the moles are there, they evolved there, too,” Catania said. Most importantly, he wanted to find out if the vibrations generated by worm grunting echo that of a digging mole and, if so, how the earthworms respond.
As they rode along, Catania noticed mole tunnels crisscrossing the backroads. He saw more around the stand of trees where Audrey and Gary worked. Catania was spellbound as he watched the couple work. Weeks later, he returned with recording equipment, marking flags, and a garden trowel. He spent hour after hour, day after day in the forest, dropping geophones into tunnel routes, hoping to record the vibrations of moles digging, as well as those produced by Gary’s grunting. For every worm Audrey picked up, he placed an orange flag in the ground, mapping just how many worms appeared, in what directions, and how far from Gary’s stob. Then, he stalked moles underground, using stakes placed along their routes to reveal where they were headed, and used the garden trowel to catch them. Back at the Revells’ place, they took a handful of worms, placed them in a five-gallon bucket, and dressed them in a pile of sawdust. Catania picked up a mole and dropped it into the bucket. The worms fled to the surface. “Okay,” Catania thought, “things are pretty clear.”
He replicated this experiment in larger bins with controlled variables. The result was the same. As soon as the mole entered the soil, the worms fled to the surface. Catania later recorded the sound of an eastern American mole digging and compared it to his recordings of Gary rooping. It was a sonic match. The vibrations were almost identical.
Catania’s work with the Revells confirmed Darwin’s theory set forth more than 125 years earlier. Worm grunters had unknowingly applied “exploitative mimicry” like that employed by herring gulls or wood turtles to lure the worms to the surface. Catania published his paper that same year in PLoS ONE, a peer-reviewed journal. The New York Times even ran a small story about his findings, as did NBC News and other outlets. Before he returned to Nashville, Catania received a parting gift from Audrey and Gary—a rooping iron that had been in their family for decades. As he drove north that day, he stopped one last time in the woods, drove a stob into the soil, and rooped with a clear sense of what was happening underground.
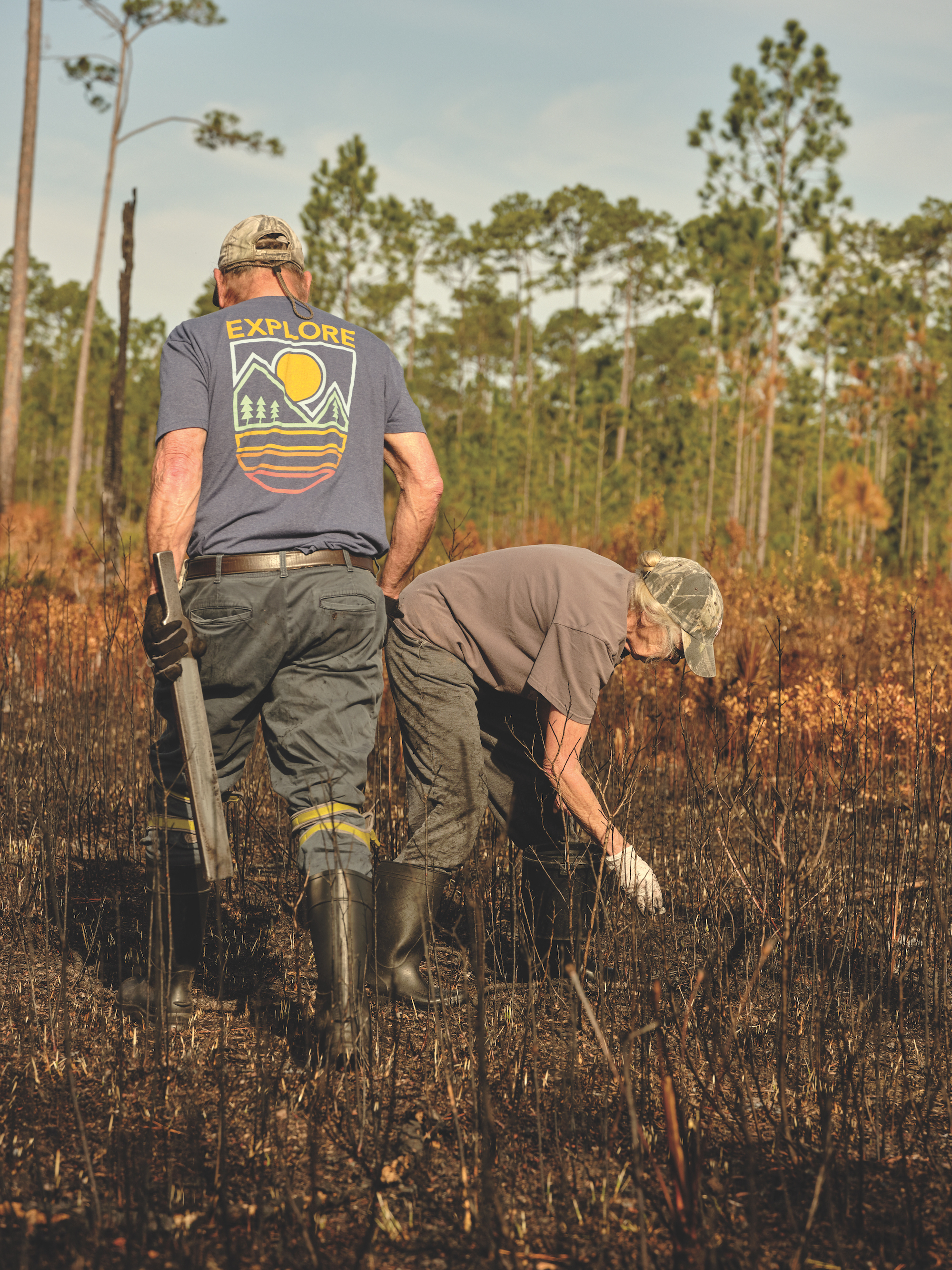

Audrey Revell collects worms by hand in the Apalachicola National Forest as Gary Revell moves to the next spot, carrying his rooping iron and stob. Photograph by Michael Adno
On my final morning with Audrey and Gary, a seam of blue sky between the pines grew brighter as they drove out into the forest. Slowly, the first signs of light threw deep shades of purple against the clouds before pink, then scarlet bands passed through the trees. “That’s beautiful,” said Audrey.
They parked their truck along the road, collected their gear, and walked into the woods. As we neared a brake of trees, Gary passed me the stob and file, pointing to a patch of earth, and I clumsily drove the stob down. I tried to place my hands on the file the same as Gary, and I slowly slid the steel at an angle. A deep noise followed, and I just smiled, rooping again and again. I varied speed and angles, making some wince-worthy goose noises on bad passes, but I found a rhythm, and soon I’d drawn up a dozen worms. I moved a few times, continuing to work, removing some layers. When I finally got up, Gary asked, “So, Mike, what do you think?” My chest throbbed and sweat ran down my neck. “It’s fucking hard work,” I said.
Back at their place, Audrey made some sweet tea and showed me a couple albums of photographs she’d made of flora and fauna in the forest. She told me of terrestrial orchids “as pretty as one you would buy,” of the pitcher plants in spring, and the white “worm flowers” that signal damp ground. “You never know what you might see,” she said. Finally, she brought out some scrapbooks and clippings of articles from the New York Times, Scientific American, and the Tallahassee Democrat. In 2010, the Revells received Florida’s Folk Heritage Award, an honor recognizing Floridians who preserve living traditions. Governor Charlie Crist presented the award in a ceremony at the state Capitol. As we looked through those reminders of their life in the forest, Audrey and Gary turned serious. “I’m a steward of this forest,” he said. “I don’t do nothing to try to abuse it or change it.” I asked Audrey what the forest meant to her. “Everything,” she said.
That afternoon, as I prepared to leave, I found myself moved in a way I hadn’t been in years, fascinated by their connection to the forest, above ground and below. “As much as we’ve done it, I’ve thought, ‘Man, you’ve got to be crazy,’” Gary said of their work. “But, if you take me away from it, I ain’t worth nothing. I’m one of the last.” I drove away with a sore palm and a cup of worms beside me.
This story was published with support from the journalism nonprofit the Economic Hardship Reporting Project as well as The Julia Child Foundation for Gastronomy and the Culinary Arts.
Did you know that the Oxford American is a non-profit?
If you enjoyed this article, consider supporting our work!
Ways to Support